What's the difference and why should you care...
First and third-party cookies are both used to track user behavior. They have similar purposes but are collected and used in different ways.
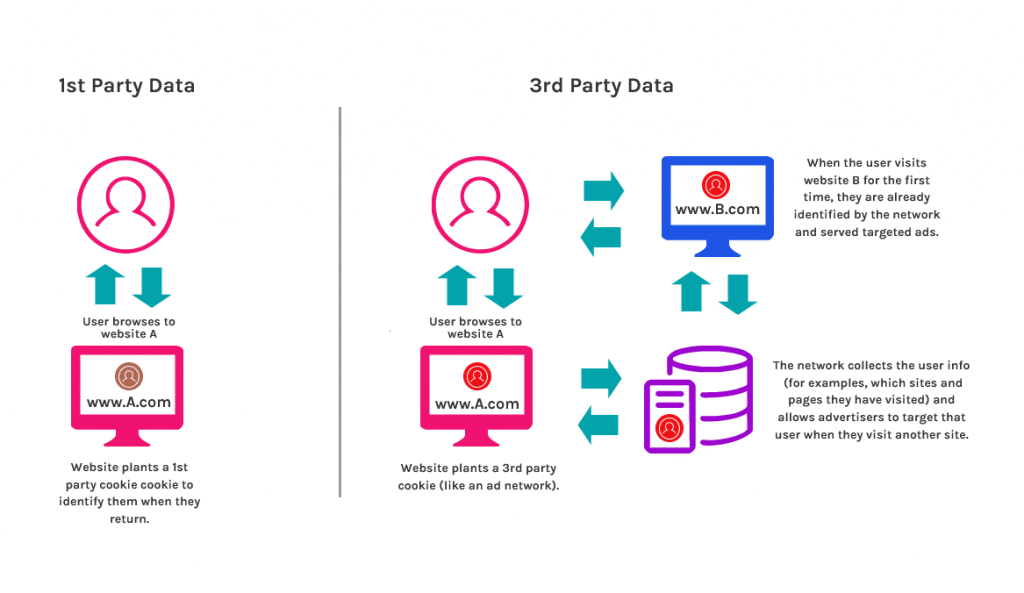
First-Party Cookies
First-party cookies are directly stored by the website (or domain) you visit. These cookies allow website owners to collect analytics data, remember language settings, and perform other useful functions that provide a good user experience.
An example of a first-party cookie is when a user signs into an e-commerce website, like Amazon. The web browser will send a request in a process that provides the highest level of trust that the user is directly interacting with Amazon. The web browser saves this data file to the user’s computer, under the “amazon.com” domain. If first-party cookies were blocked, a user would have to sign-in every time they visited, and they wouldn’t be able to purchase multiple items while shopping online because the cart would reset after every item that was added.
Third-Party Cookies
Third-party cookies are created by domains that are not the website (or domain) that you are visiting. These are usually used for online-advertising purposes and placed on a website through a script or tag. A third-party cookie is accessible on any website that loads the third-party server’s code.
Similar to the previous example, third-party cookies work when a user researching information on a topic on a sight like TechTarget. Then tech target sells that cookie to brands who want to advertise to a potential buyer of a product that relates to the topic browsed. Even if the user closes their browser and ends the session, that tracking data will still be on their computer.
Differences between First and Third Party Cookies
The main differences between first and third-party cookies include:
- Setting the cookie: A first-party cookie is set by the publisher’s web server or any JavaScript loaded on the website. A third-party cookie can be set by a third-party server, such as a Publisher Network like Bombora, Aberdeen or Tech Target, or via code loaded on the publisher’s website.
- Cookie availability: First-party cookies are available to the domain that created it. A third-party cookie is accessible on any website that loads the third-party server’s code.
- Browser support/blocking: First-party cookies are supported by all browsers and can be blocked or deleted by the user. Third-party cookies are supported by all browsers, but many are blocking the creation of third-party cookies by default. Users are also taking matters into their own hands and deleting third-party cookies on their own.
Gregory Kotovos • November 3, 2021


